
Book value is the accounting value of the company’s assets less all claims senior to common equity (such as the company’s liabilities). The book value per share of an undervalued stock is higher than its current market price, so book value per share can help investors appraise a stock price. Although infrequent, many value investors will see a book value of equity per share below double entry accounting the market share price as a “buy” signal. But an important point to understand is that these investors view this simply as a sign that the company is potentially undervalued, not that the fundamentals of the company are necessarily strong. The difference between a company’s total assets and total liabilities is its net asset value, or the value remaining for equity shareholders.
Market Capitalisation = Market Value of a Stock x Number of Outstanding Shares
Therefore, the amount of cash remaining once all outstanding liabilities are paid off is captured by the book value of equity. Therefore, the book value per share (BVPS) is a company’s net asset value expressed on a per-share basis. This means that each share of the company would be worth $8 if the company got liquidated.
Deceptive Depreciation and Book Value
A company can use a portion of its earnings to buy assets that would increase common equity along with BVPS. Or, it could use its earnings to reduce liabilities, which would also increase its common equity and BVPS. A P/B ratio below 1 often indicates that a company’s stocks are undervalued since its market capitalisation is lower than its book value. Similarly, a high P/B ratio might imply that a company’s stocks are overvalued. Some investors go for the per-share approach, thereby dividing the shareholder’s equity by the number of outstanding shares, i.e.
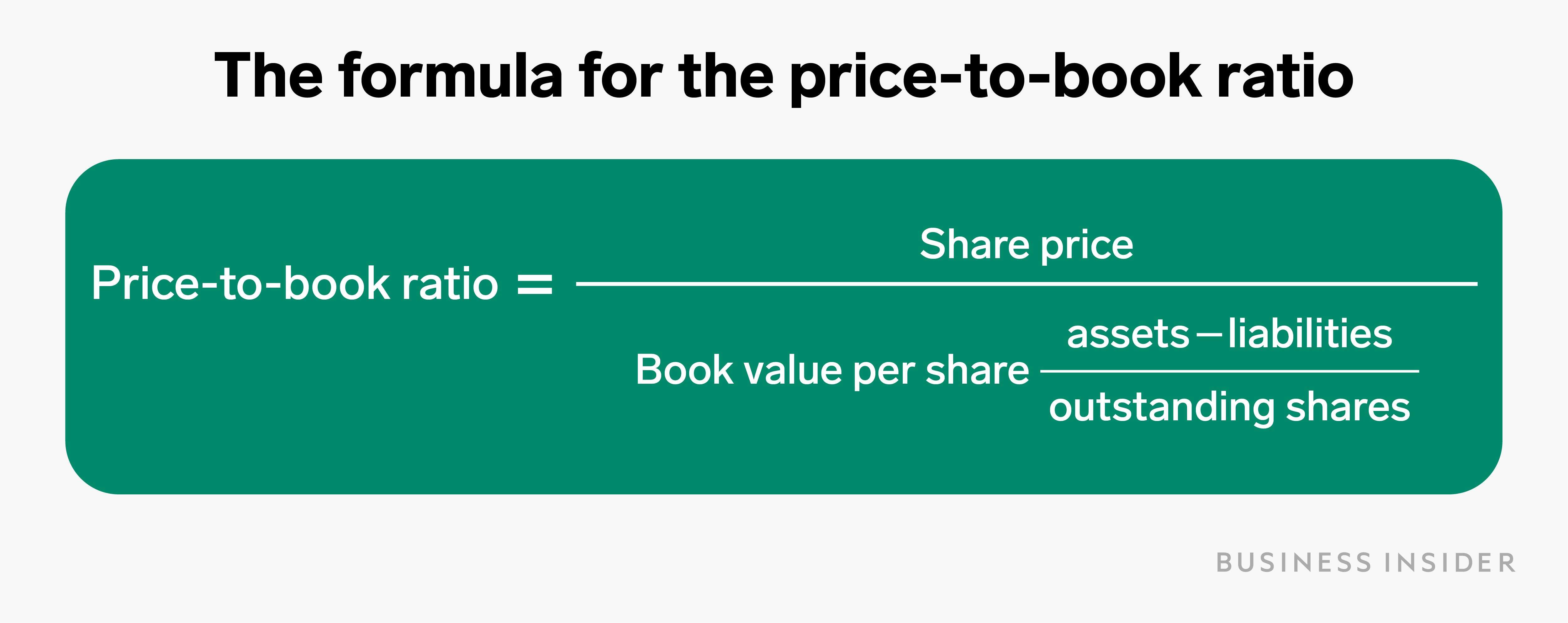
Limitations of Using the Price-to-Book (P/B) Ratio
The next assumption states that the weighted average of common shares outstanding is 1.4bn. Price-to-book (P/B) ratio as a valuation multiple is useful when comparing similar companies within the same industry that follow a uniform accounting method for asset valuation. It can offer a view of how the market values a particular company’s stock and whether that value is comparable to the BVPS. There is a difference between outstanding and issued shares, but some companies might refer to outstanding common shares as issued shares in their reports. If a company has a book value per share that’s higher than its market value per share, it’s an undervalued stock.
Book Value Per Share Calculation Example (BVPS)
She supports small businesses in growing to their first six figures and beyond. Alongside her accounting practice, Sandra is a Money and Life Coach for women in business. Conversely, if the market value per share exceeds BVPS, the stock might be perceived as overvalued. BVPS offers a baseline, especially valuable for value investors looking for opportunities in underpriced stocks. On the other hand, if a company with outdated equipment has consistently put off repairs, those repairs will eat into profits at some future date.
It takes the net value of a listed company’s assets, also known as shareholder’s equity, and divides it by the total number of outstanding shares of that organisation. The figure that represents book value is the sum of all of the line item amounts in the shareholders’ equity section on a company’s balance sheet. As noted above, another way to calculate book value is to subtract a business’ total liabilities from its total assets.
Investors use BVPS to gauge whether a stock price is undervalued by comparing it to the firm’s market value per share. Book value refers to a firm’s net asset value (NAV) or its total assets minus its total liabilities. Assume that XYZ Manufacturing has a common equity balance of $10 million and 1 million shares of common stock are outstanding. This means that the BVPS is ($10 million / 1 million shares), or $10 per share. If XYZ can generate higher profits and use those profits to buy assets or reduce liabilities, the firm’s common equity increases. A metric that investors use with regard to book value is BVPS or Book Value of Equity per Share.
The following image shows Coca-Cola’s “Equity Attributable to Shareowners” line at the bottom of its Shareowners’ Equity section. In this case, that total of $24.1 billion would be the book value of Coca-Cola. It’s one metric that an investor may look for if they’re interested in valuating Coca-Cola as a potential investment. Even though book value per share isn’t perfect, it’s still a useful metric to keep in mind when you’re analyzing potential investments. BVPS is more relevant for asset-heavy companies, such as manufacturing firms, where physical assets constitute a significant portion of the balance sheet. As demonstrated in this example, many investors believe that B is a better-valued firm because of its relatively lower P/B ratio.
Rather than buying more of its own stock, a company can use profits to accumulate additional assets or reduce its current liabilities. For example, a company can use profits to either purchase more company assets, pay off debts, or both. These methods would increase the common equity available to shareholders, and hence, raise the BVPS.
- Therefore, the book value of Company Arbitrary would be the difference between its total assets and total liabilities.
- Using the same share basis formula, we can calculate the book value per share of Company B.
- To get BVPS, you divide the figure for total common shareholders’ equity by the total number of outstanding common shares.
For example, if the BVPS is greater than the MVPS, the company’s stock market may be undervaluing a company’s stock. Should the company dissolve, the book value per common share indicates the dollar value remaining for common shareholders after all assets are liquidated and all creditors are paid. Now, let’s say that Company B has $8 million in stockholders’ equity and 1,000,000 outstanding shares. Using the same share basis formula, we can calculate the book value per share of Company B. Book Value Per Share is calculated by dividing the total common equity by the number of outstanding shares. Second, the net worth of an organization’s assets must be ascertained by investors.
Post a Comment